Thermal comfort is not possible where the air temperature and the mean radiant surface temperature differ by more than 5 c.
How to thermal break floor concrete for temperature difference.
Physics concrete is the perfect material to satisfy the requirements for human thermal comfort.
The thermal break insulates the interior floor slab from the exterior exposed slab edge while transferring the loads imposed on the exposed slab edge back to the interior floor slab.
Additionally as cement mixes with water a chemical reaction called hydration occurs generating heat.
The physics of heat flow in buildings is the reason why.
Of course the temperature difference is an external factor.
R value is 1 divided by btus per hour persquare foot per degree f.
Thermal break materials are characterized either by their thermal conductivity k or thermal resistance r.
The rebar on the top of the thermal break acts as a tension member to support the cantilevered balcony slab.
The rate of heat transfer at any given temperature difference falls with increasing r value and r value is the determining factor of a thermal break.
This temperature difference is the difference between the temperature at the hottest portion of the concrete and that at the surface.
Poly above the concrete and below the subfloor should stop moisture from causing problems from below.
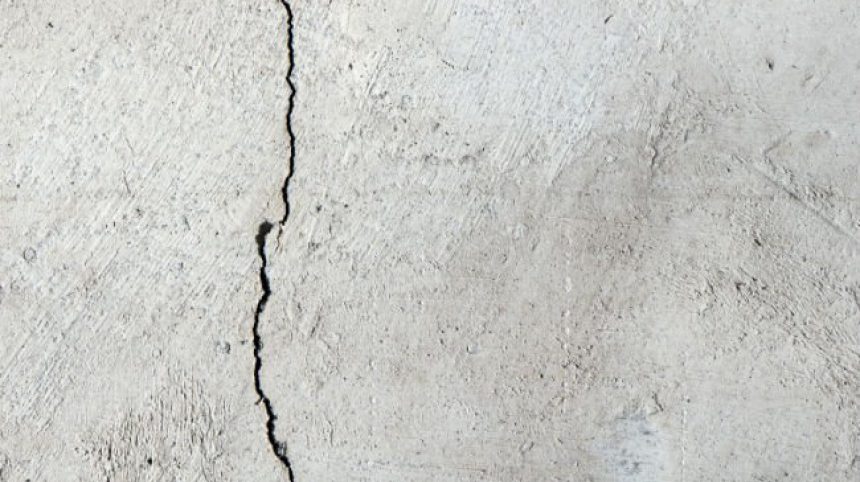
Thermal cracking occurs when the tensile stress of the concrete exceeds its tensile strength.
A schöck isokorb structural thermal break is a fabricated assembly that is cast into the concrete floor slab at the location of the building insulation layer.
A maximum allowable concrete temperature difference is often specified to minimize the potential for thermal cracking.
The thermal conductivity of normal conventional concrete depends on its composition and when the concrete is saturated the conductivity ranges generally between about 1.
Thermal conductivity is the rate at which heat is transmitted through a material of unit area and thickness when there is a unit difference in temperature between the two faces.
The thickness and the conductivity are properties of the material.
The heat flow through a building construction depends on the temperature difference across it the conductivity of the materials used and the thickness of the materials.
The thermal break with 30 inch stainless steel reinforcing bars protruding from the top on each side is positioned at the edge of the slab and wire tied to the interior steel.
In more basic terms differences in temperature between the core of the concrete and its surface can lead to thermal cracks.
Thermal contraction on the concrete s surface without a corresponding change in its interior temperature will cause a thermal differential and potentially lead to cracking.